Topics
Table of Contents
What Is a Coma?
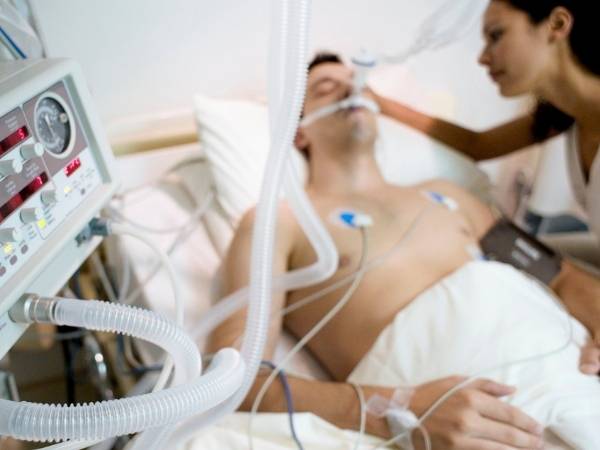
A coma is a state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person is unresponsive to external stimuli and unable to wake up. Individuals in a coma appear as if they are in a deep sleep and do not exhibit purposeful movements or responses. Comas can result from various medical conditions, including traumatic brain injuries, strokes, severe infections, metabolic disorders, or drug overdoses.
Comas are generally considered a medical emergency, and individuals in a coma require immediate medical attention. The severity and potential outcomes of a coma can vary depending on the underlying cause and the extent of damage to the brain.
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a commonly used tool to assess the level of consciousness in individuals with brain injuries or other conditions affecting the brain. It evaluates eye, verbal, and motor responses to stimuli and assigns a score that helps healthcare professionals classify the level of consciousness, with lower scores indicating more severe impairment.
It’s important to note that a coma is different from a vegetative state. In a coma, the person is completely unconscious, whereas in a vegetative state, there may be some level of wakefulness without meaningful awareness or responsiveness.
The prognosis for individuals in a coma varies widely depending on the cause, the duration of unconsciousness, and the effectiveness of medical interventions. Some individuals may gradually regain consciousness and recover, while others may experience long-term disability or may not recover at all. Medical professionals play a crucial role in assessing and managing individuals in a coma, providing supportive care, and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
Brain Death
Brain death refers to the irreversible cessation of all cerebral and brainstem activities, leading to the complete and permanent loss of brain function. When an individual is declared brain dead, it means that there is no blood flow to the brain, and the brain has permanently stopped functioning. Brain death is a legal and medical definition of death.
The criteria for determining brain death vary by jurisdiction but generally include the absence of all neurological activity, as confirmed by thorough clinical and neurological examinations. In some cases, additional tests, such as electroencephalography (EEG) and cerebral blood flow studies, may be performed to support the diagnosis.
It’s important to distinguish brain death from a coma or a vegetative state. In a coma, there is still some brain activity, and the individual may have the potential for recovery. In a vegetative state, there might be partial brain function, but the person lacks awareness and meaningful responsiveness.
The declaration of brain death is a sensitive and carefully regulated process, often involving multiple assessments by different healthcare professionals. Ethical considerations and legal guidelines vary across regions, and healthcare providers follow established protocols to ensure accuracy and reliability in determining brain death.
Once brain death is declared, the person is legally dead, and life support systems may be withdrawn. Organ donation may be considered if the individual or their family has consented to it. Brain death is a complex and emotionally charged topic, and decisions related to it involve close collaboration between medical professionals, patients’ families, and, in some cases, legal authorities.
Vegetative State
A vegetative state is a condition of severely impaired consciousness in which a person is awake but shows no signs of awareness or meaningful responsiveness to their environment. Individuals in a vegetative state may have basic reflexes, such as eye movement or the ability to breathe on their own, but they lack higher cognitive function and are unable to communicate or exhibit purposeful behavior.
This state can result from various causes, including traumatic brain injury, oxygen deprivation, severe infections, or certain neurological disorders. It is important to note that a vegetative state is distinct from a coma. In a coma, a person is in a deep state of unconsciousness and does not exhibit any signs of wakefulness. If a person remains in a vegetative state for an extended period, it may be considered a persistent vegetative state.
The assessment and diagnosis of a vegetative state can be complex, and it often involves careful observation and evaluation by medical professionals. The prognosis for recovery from a vegetative state varies depending on the underlying cause and the extent of brain damage. In some cases, individuals may progress to a minimally conscious state, where there is minimal but detectable evidence of awareness.
It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate information about an individual’s specific condition and prognosis. Additionally, discussions about the ethical and legal aspects of managing individuals in a vegetative state may arise, particularly concerning decisions about medical care and end-of-life considerations.
Coma Vs. Brain Death Vs. Vegetative State
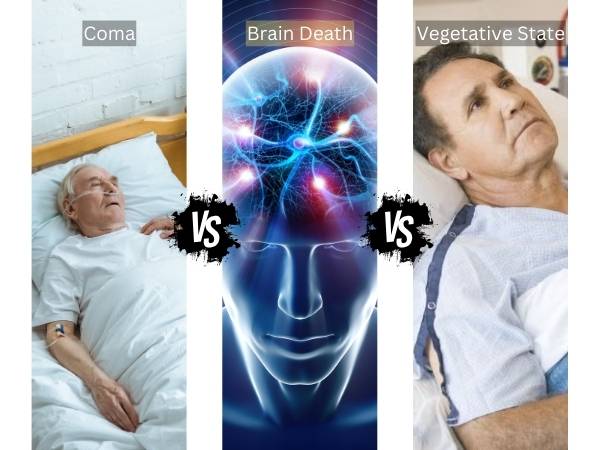

Coma:
- Definition: A coma is a state of profound unconsciousness where an individual is unresponsive to external stimuli and cannot be awakened. It is typically the result of severe injury, illness, or trauma affecting the brain.
- Characteristics: In a coma, the person appears as if in a deep sleep, with closed eyes and no purposeful responses. They do not react to stimuli such as sounds, pain, or light.
- Duration: Comas can be short-term or long-term. Short-term comas may resolve spontaneously, while long-term comas may indicate more severe brain damage.
- Brain Function: While in a coma, there is often some residual brain activity, and individuals may exhibit basic reflexes. The potential for recovery depends on the underlying cause and the extent of brain damage.
Brain Death:
- Definition: Brain death is the irreversible cessation of all cerebral and brainstem activities, resulting in the permanent loss of all brain functions. It is a legal and medical definition of death.
- Characteristics: When an individual is declared brain dead, there is a complete absence of brain activity, including in the cerebral cortex and brainstem. The person is considered legally and clinically dead.
- Irreversibility: Brain death is irreversible, and there is no possibility of recovery. Life support systems may be withdrawn after careful confirmation of the diagnosis and in accordance with legal and ethical considerations.
- Organ Donation: In some cases, if the individual or their family consents, organ donation may be considered after brain death is declared.
Vegetative State (Unresponsive Wakefulness Syndrome)
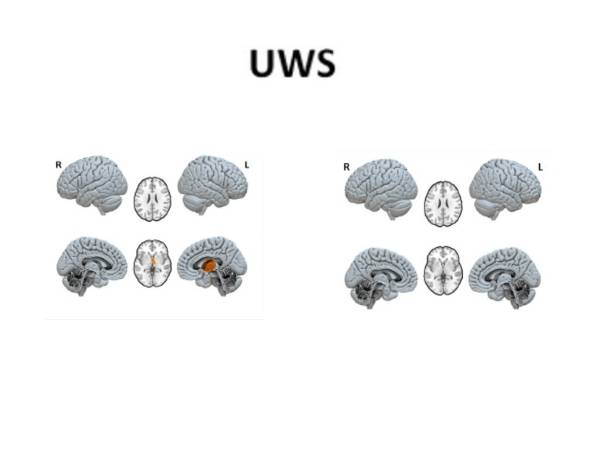
Definition: A vegetative state is a condition of severely impaired consciousness where an individual may appear awake but lacks meaningful awareness and responsiveness to the environment.
- Characteristics: Individuals in a vegetative state may exhibit basic reflexes such as eye movement or spontaneous body movements. They may open their eyes and may display sleep-wake cycles, but there is no purposeful behavior or communication.
- Brain Function: Unlike brain death, there is still some level of preserved brain function in a vegetative state, but it is not sufficient for higher cognitive functions or awareness.
- Prognosis: The prognosis for recovery from a vegetative state varies, and some individuals may progress to a minimally conscious state with limited awareness.
In summary, coma is a state of profound unconsciousness with potential for recovery, brain death is the irreversible cessation of all brain activity resulting in legal and clinical death, and a vegetative state involves impaired consciousness with some preserved reflexes but without meaningful awareness or responsiveness. Each condition has distinct characteristics and implications for medical care and ethical considerations.