Topics
Table of Contents
Brain Ischemia, also known as cerebral ischemia, refers to a condition characterized by a decrease in blood supply to the brain, resulting in inadequate oxygen and nutrient delivery to brain tissues. This lack of blood flow can lead to serious consequences, including stroke and brain damage. Understanding the types, signs, symptoms, causes, prevention strategies, treatment options, diagnosis, and home remedies for brain ischemia is crucial for the effective management and prevention of this condition.
Types of Brain Ischemia
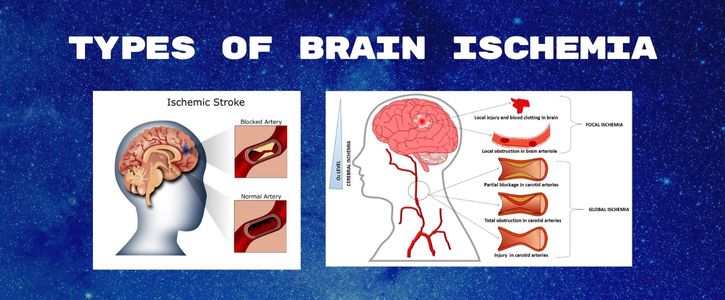
- Ischemic Stroke: This occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery supplying blood to the brain.
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Often referred to as a “mini-stroke,” it is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, usually lasting for a few minutes. TIAs typically do not cause permanent damage but can be warning signs of an impending stroke.
- Global Ischemia: This occurs when blood flow to the entire brain is significantly reduced or interrupted, often due to cardiac arrest or severe hypotension.
- Focal Ischemia: It affects a specific region of the brain and can result from various causes, including embolic or thrombotic events.
Signs and Symptoms

The signs and symptoms of brain ischemia can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the specific areas of the brain affected. Common symptoms may include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness, often on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision disturbances
- Severe headache
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Confusion or cognitive impairment
- Difficulty walking or coordinating movements
Causes of Brain Ischemia

Brain ischemia typically occurs due to the following reasons:
- Blood Clots: Formation of blood clots in the arteries supplying blood to the brain.
- Atherosclerosis: Build-up of plaque in the arteries, leading to narrowing and reduced blood flow.
- Heart Conditions: Conditions such as atrial fibrillation or heart valve disorders can increase the risk of blood clots traveling to the brain.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels, contributing to the risk of ischemic events.
- Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of atherosclerosis and blood clot formation.
- Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: These factors contribute to hypertension, diabetes, and atherosclerosis, further increasing the risk of brain ischemia.
Prevention Strategies

Several lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help prevent brain ischemia:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Control hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation significantly reduces the risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can increase blood pressure and contribute to stroke risk.
- Monitor Heart Health: Manage conditions such as atrial fibrillation and heart valve disorders under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for multiple cardiovascular conditions, including brain ischemia.
Treatment Options

Treatment for brain ischemia aims to restore blood flow to the brain, prevent further damage, and address underlying risk factors. Treatment options may include:
- Clot-Busting Medications: Thrombolytic drugs such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) can dissolve blood clots and restore blood flow during an acute ischemic stroke.
- Antiplatelet Medications: Drugs like aspirin or clopidogrel may be prescribed to prevent blood clot formation.
- Anticoagulants: These medications, such as warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), can help prevent blood clot formation in individuals at high risk.
- Carotid Endarterectomy: Surgical removal of plaque from the carotid arteries to improve blood flow to the brain.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: In some cases, a minimally invasive procedure may be performed to open narrowed arteries and improve blood flow.
- Rehabilitation Therapy: Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy may be necessary to help individuals regain lost function and improve their quality of life after a stroke or brain ischemia.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing brain ischemia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Imaging Studies: CT scans, MRI scans, and angiography can help visualize brain structures, identify blockages, and assess blood flow.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test evaluates heart rhythm and can detect abnormalities that increase the risk of stroke.
- Blood Tests: Laboratory tests may be performed to assess cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and other markers of cardiovascular health.
Home Remedies

While medical treatment is essential for managing brain ischemia, certain home remedies and lifestyle changes may also support recovery and reduce the risk of recurrent events:
- Healthy Eating: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress levels.
- Limit Salt Intake: Reduce salt consumption to help control blood pressure.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water each day to maintain hydration and support overall health.
- Get Sufficient Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night to support brain health and overall well-being.
- Avoid Tobacco and Excessive Alcohol: Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
In conclusion, brain ischemia is a serious medical condition that requires prompt recognition and intervention to minimize the risk of complications such as stroke and permanent brain damage. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying risk factors, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can reduce their risk of brain ischemia and improve their overall brain health and well-being. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized prevention and treatment plan tailored to individual needs and medical history.