Topics
Table of Contents
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic and potentially disabling autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, comprising the brain and spinal cord. This condition disrupts the flow of information within the brain and between the brain and the rest of the body. In this blog, we will explore the various aspects of multiple sclerosis, including its types, signs, symptoms, causes, prevention, treatment, diagnosis, and home remedies.
Types of Multiple Sclerosis
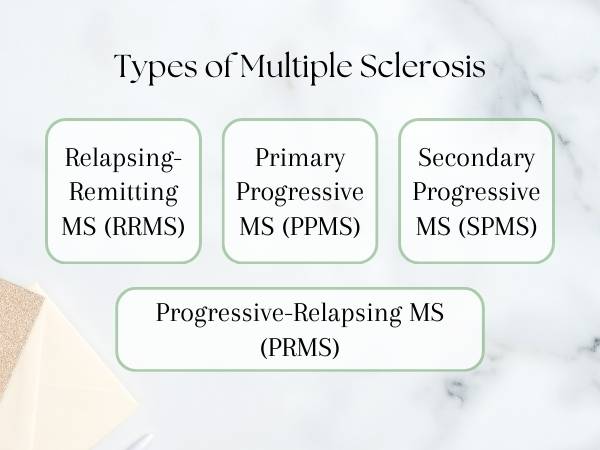
- Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS): This is the most common form of MS, characterized by periods of new symptoms or relapses followed by periods of remission where symptoms improve partially or completely.
- Primary Progressive MS (PPMS): This form involves a steady progression of symptoms without distinct relapses or remissions.
- Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS): Initially, individuals with RRMS may transition to SPMS, where symptoms progressively worsen over time with or without periods of remission.
- Progressive-Relapsing MS (PRMS): This is the least common type, characterized by a steady progression of the disease with occasional relapses.
Signs and Symptoms

The signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis can vary widely among individuals. Common manifestations include:
- Fatigue: A pervasive and often overwhelming sense of exhaustion.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision, double vision, or partial or complete loss of vision.
- Coordination and Balance Issues: Difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
- Muscle Weakness and Spasms: Weakness or spasms in the muscles, often affecting the legs.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles” in various parts of the body.
- Cognitive Impairment: Problems with memory, attention, and problem-solving.
- Pain: Chronic pain, often affecting the back or muscles.
Causes

The exact cause of multiple sclerosis remains unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential triggers include:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of MS are at a slightly higher risk.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain viruses, low vitamin D levels, and smoking have been associated with an increased risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: MS is considered an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers (myelin).
Prevention
While there is no definitive way to prevent multiple sclerosis, certain lifestyle choices may help reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may contribute to overall health.
- Adequate Vitamin D: Sunlight exposure and/or vitamin D supplements may be beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help improve overall health and well-being.
Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)

There is currently no cure for multiple sclerosis, but various treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Treatment options include:
- Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs): Medications that modify or suppress the immune response to reduce inflammation and slow down the progression of the disease.
- Symptomatic Treatments: Medications and therapies to alleviate specific symptoms, such as muscle spasms, pain, and fatigue.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: Exercises and strategies to improve mobility, strength, and daily functioning.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis involves a combination of medical history, neurological examinations, and diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Used to detect lesions or areas of damage in the central nervous system.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis: Examination of the fluid around the brain and spinal cord to check for abnormalities.
- Evoked Potentials: Tests that measure electrical activity in the brain in response to stimuli.
Home Remedies for Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
While home remedies cannot replace medical treatment, they may offer some relief from certain symptoms:
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat packs or warm baths may help alleviate muscle stiffness and spasms.
- Regular Exercise: Tailored exercises can improve strength, flexibility, and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Practices such as meditation and yoga may help manage stress, which can exacerbate MS symptoms.
In Conclusion, Multiple sclerosis is a complex and challenging condition, but advancements in research and treatment options provide hope for those affected. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with MS. As with any medical condition, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.